IT Event Management Process explained!
IT Event Management: Strategies and Best Practices
Purpose & Scope
Purpose
The objective of Event Management process is to monitor all events that occur through the <Customer’s Name> IT infrastructure & application to allow for normal operations & also to detect and escalate exception conditions to service desk of AMS.
Scope
The scope of this process includes the customer’s IT infrastructure & application which is under the control of service desk of AMS.
Definitions
Event
An Event can be defined as any detectable occurrence that has significance for management of <Customer’s Name> IT infrastructure & application or the delivery of <Customer’s Name> IT Service.
Alert
An Alert can be defined as a warning that a threshold has been reached, something has changed, or a Failure has occurred.
Configuration Item (CI)
Configuration Item is any component that needs to be managed in order to deliver <Customer’s Name> IT Service.
Roles and Responsibilities
Operations Control Function responsibilities
- Oversees the execution & monitoring of the operational activities.
- Define central observation & monitoring capability and then using those consoles to exercise monitoring & control activities (Console management).
- Management of routine batch jobs or scripts (Job Scheduling).
- Backup & restore operations.
Service desk responsibilities
- Response to the alerts if required.
- Undertaking Incidents that have been identified by Event management and escalate to appropriate team.
Application Management Team responsibilities
- Participate in instrumentation of service, classify events and ensure the auto-responses are defined.
- Test the service to ensure the events are properly getting generated and the defined responses are appropriate.
- Deal with the Incidents & problems related to events.
- Perform Event management activities for the systems which are under the control of Application Management Service (AMS).
Input, Output
Inputs
- Event
- Threshold and Exception rules
- Instrumentation Decisions
- Thresholds
Outputs
- Communications
- Notifications
- Incident
- Problem
- Change
Event Management Process flow
The ability to detect events, make sense of them and determine the appropriate control action is provided by Event Management. Event Management is therefore the basis for Operational Monitoring and Control of <Customer’s Name> IT infrastructure.
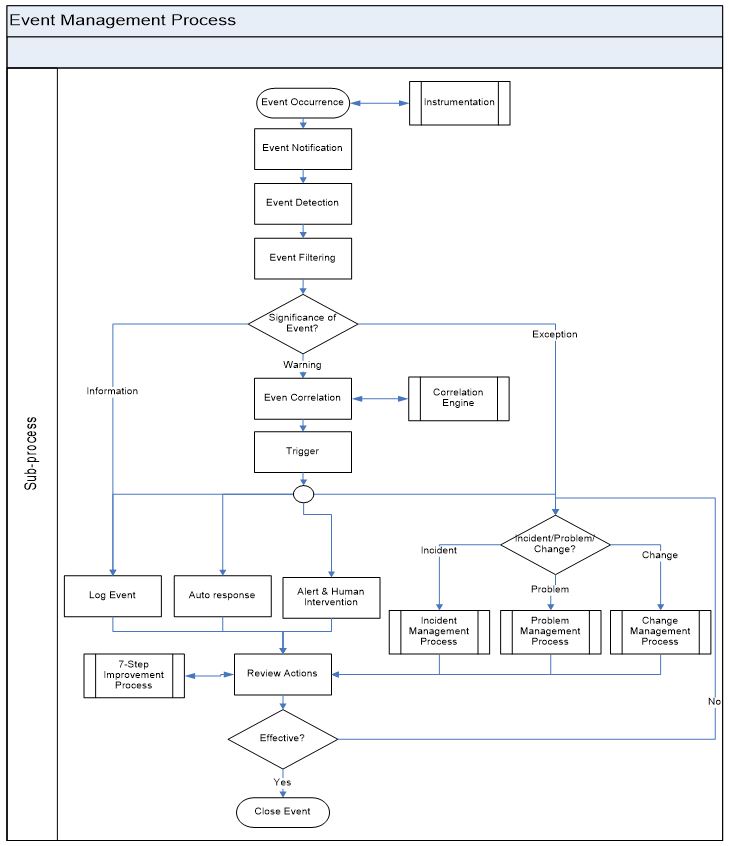
Event Management Process flow detailed description
| Activity No. | Step | Description | Input-Output | Role |
| 1 | Event Occurrence | Events occur continuously, not all of them will be detected & registered. It is important to understand what type of events needs to be detected. | Input Instrumentation decisions Event Output Detected event |
– |
| 2 | Instrumentation | Define what needs to be monitored about CI’s and the way to monitor them. Define & design exactly what to monitor & how to monitor and control the IT Service. “Instrumentation decisions & mechanism checklist” provides the basis for key decisions & mechanism for Instrumentation. | Output Instrumentation decisions |
Application Management Team |
| 3 | Event Notification | CIs should be configured to generate a standard set of events, based what is required to operate the CI. A general principle of Event notification is that the more meaningful the data it contains and the more targeted the audience, the easier it is to make decisions about the event. | Input Event Output Event Notification |
Automated Tool |
| 4 | Event Detection | Once an Event notification has been generated, it should be detected to read and interpret the meaning of the event. | Input Output | Automated Tool |
| 5 | Event Filtering | The first level of correlation will be performed here. Determine weather the event is informational, warning or exception. | Input Detected Event Output Informational/Warning/Exception |
Operations Control/Automated Tool |
| 6 | Significance of Event? |
Categorize the significance of the event into the below mentioned broad categories: Informational: This refers to an event that does not require any action and does not represent an exception. These events are typically used to check the status of a device or service, or to confirm the successful completion of an activity. Warning: A warning is an event that is generated when a service or device is approaching a threshold. Warnings are intended to notify that the situation can be checked and the appropriate action taken to prevent an exception. Exception: An exception means that a service or device is currently operating abnormally. This means that SLA has been breached and the business is getting impacted. Exceptions could represent a total failure, impaired functionality or degraded performance. |
Output Categorization of event |
Operations Control |
| 7 | Even Correlation | If an event is significant, a decision has to be made about exactly what the significance is and what actions need to be taken to deal with it. Correlation will be done using “Correlation engine” which compares the event with a set of criteria & rules. A correlation engine is programmed according to the performance requirements. Correlation Engine also matches the events to check the similarity between the events. | Input Event Output Required response |
Operations Control /Automated Tool |
| 8 | Trigger | This is the mechanism to initiate the required response recognized by correlation engine. At this point of the time there are number of response options available. These response actions can be chosen in any combination. | Input Required response Output Response actions |
Operations Control /Automated Tool |
| 9 | Log Event | Log the event in the Event Management tool or in a system log regardless of what activity is performed. | Input Event Output Event Log |
Operations Control /Automated Tool |
| 10 | Auto response | Events that are understood well enough that the appropriate response has already been defined and automated. The trigger will initiate the action and then evaluate whether it was completed successfully. If not, an Incident or Problem Record will be created. | Input Event Output Auto Response |
Automated Tool |
| 11 | Alert & Human Intervention | The event will be escalated if it requires human intervention. The alert will contain all the information necessary for that person to determine the appropriate action. | Input Event |
Operations Control /Automated Tool |
| 12 | Incident/Problem/Change? | For the events which will represent a situation where the appropriate response will need to be handled through the Incident, Problem or Change Management process. A single event may initiate any one or a combination of these three processes. | Input Event Output Incident/Problem/Change |
Operations Control /Automated Tool |
| 13 | Review Actions | For the significant events & exception, review will happen to check the way the events got handled. Review the handover with other processes. Review results will be input to the Improvement process. | Input Event Log Output Improvement actions Corrective actions |
Application Management Team |
| 14 | Effective? | Check the effectiveness of the actions on the Event and take the appropriate actions. If the results are satisfactory proceed to the closure otherwise invoke Incident/Problem/Change Management process as required. | Input Event Log Output Actions identified |
Application Management Team |
| 15 | Close Event | All the events which got logged should formally get closed. Events should be linked to appropriate Incident/Problem/Change records. | Input Event Log Output Closed Event |
Operations Control |
References
Measurements
Reports are generated based on the below metrics.
| Metrics | Description |
| Number of Events by category | Occurrence of events in each category, which will indicate the performance. |
| Number of events by significance | Number events generated, which are Informational, Warnings & Exceptions. |
| Number & percentage of events required human intervention | How many incidents required human intervention, which will indicate the opportunity for automation. |
| Number and percentage of events resulted in incidents and changes | Indicate the percentage of events that resulted in Incidents & changes. |
| Number and percentage of repeated/duplicate events | This will help to finetune the correlation engine |
| Number Events routed for the review | This will help to understand the effectiveness of event management |
Authored by Vijay Chander – All rights Reserved – 2023