Process flow for Release and Deployment Management
Process flow for Release and Deployment Management
Purpose & Scope
Purpose
The purpose of Release and deployment Management process is to:
- Define and agree release and deployment plans with <Customer’s Name> and stakeholders.
- Ensure that each release package consists of a set of related assets and service components that are compatible with each other.
- Maintain the integrity of a release package and its constituent components throughout the transition activities and accurately record them in the CMS.
- Ensure that you can track, install, test, verify, and, if necessary, uninstall or back out all release and deployment packages..
- Ensure active management of organizational and stakeholder change during release and deployment activities.
- Record and manage deviations, risks, issues related to the new or changed service and take necessary corrective action.
- Ensure that there is knowledge transfer to enable the <Customer’s Name> and its users to optimize their use of the service to support their business activities.
- Ensure the effective and efficient delivery, support, and maintenance of the service according to required service levels by transferring skills and knowledge to operations and support staff…
Scope
The scope of the Release and Deployment Management Process encompasses packaging, building, testing, and deploying a release into production for , including their processes, systems, and functions within the defined frozen scope, to establish the desired service.
Definitions
Release
A collection of hardware, software, documentation, Processes or other Components required to implement one or more approved Changes to <Customer Name>’s IT Service. Manage, test, and deploy the contents of each release as a single entity.
Change
The addition, modification or removal of anything that could have an effect on <Customer Name>’s IT Service.
Configuration Management System (CMS)
It is a set of tools and databases that are used to manage your organization’s Configuration data.
This includes tools for collecting, storing, managing, updating, and presenting data about all CI and their Relationships.
The CMS also includes information about Incidents, Problems, Known Errors, Changes and Releases; and may contain data about employees, Suppliers, locations, Business Units, Customers and Users
The CMS is maintained by Configuration Management and is used by all Service Management Processes.
Configuration Item
CI is any component that needs to be managed in order to deliver <Customer’s Name> IT Service.
Configuration Baseline
It is a Baseline of a Configuration Items that has been formally agreed and is managed through the Change Management process that is decided by your organization.
A Configuration Baseline is used as a basis for future Builds, Releases and Changes.
Service Knowledge Management System (SKMS)
It is a set of tools and databases that are used to manage knowledge and information. The SKMS includes the Configuration Management System (CMS), Known Error Data Base (KEDB) as well as other tools and databases. The SKMS stores, manages, updates, and presents all information that an IT Service provider needs to manage the full Lifecycle of <Customer Name>’s IT Services.
Service Asset
It can be any Resource or Capability that contribute to the delivery of a service.
Assets can be of the following types: Management, Organization, Process, Knowledge, People, Information, Applications, Infrastructure and financial capital.
Roles and Responsibilities
Release and Deployment Manager
Responsibilities
- Manages all aspects of the end-to-end release process.
- Updates the SKMS and CMS.
- Ensures coordination of build and test environment team and release teams.
- Ensures teams follow the organization’s established policies and procedures.
- Provides management reports on release progress.
- Release and deployment policy and planning.
- Deals with release package design, build and configuration.
- Deals with release package acceptance including business sign-off.
- Deals with service roll-out planning including method of deployment.
- Deals with release package testing to predefined Acceptance Criteria.
- Signs off the release package for implementation.
- Deals with communication, preparation and training.
- Audits hardware and software before and after the implementation of release package changes.
- Installs new or upgraded hardware.
- Deals with storage and traceability/audit-ability of controlled software in both centralized and distributed systems.
- Deals with release, distribution and the installation of packaged software.
Release Packaging & Build Manager
Responsibilities
- Establishes the final release configuration (e.g. knowledge, information, hardware, software and infrastructure).
- Builds the final release delivery.
- Tests the final delivery prior to independent testing.
- Establishes and reports outstanding known errors and workarounds.
- Provides input to the final implementation sign-off process.
Deployment Staff
Responsibilities
- Deal with the final physical delivery of the service implementation.
- Coordinate release documentation and communications, including training and customer, Service Management and technical release notes.
- Plan the deployment in conjunction with change and Knowledge Management and Service Asset & Configuration Management.
- Provide technical and application guidance and support throughout the release process, including known errors and workarounds.
- Provide feedback on the effectiveness of the release.
- Record metrics for deployment to ensure within agreed SLAs.
Early life support staff
Responsibilities
- Provide <Customer Name>’s IT service and business functional support from prior to final acceptance by Service Operations.
- Ensure delivery of appropriate support documentation.
- Provide release acceptance for provision of initial support.
- Provide initial support in response to incidents and errors detected within a new or changed service.
- Adapt and perfect elements that evolve with initial usage, such as:
- User documentation
- Support documentation including service desk scripts
- Data management, including archiving
- Embed activities for a new or changed service
- Deal with formal transition of the service to Service Operations.
- Monitor incidents and problems, and undertake problem management during release and deployment, raising RFCs as required.
- Provide initial performance reporting and undertake service risk assessment based on performance.
Build & Test Environment Staff
Responsibilities
- Ensure service infrastructure and application are built to design specification.
- Plan acquisition, build, implementation and maintenance of the infrastructure
- Ensure build delivery components are from controlled sources
- Develop an integrated application software and infrastructure build
- Deliver appropriate build, operations and support documentation for the build and test environments prior to handover to Service Operations
- Build, deliver and maintain required testing environments.
Input, Output
Inputs
- Request For Change (RFC)
- Service Package
- Continuity Plan
- Service Management Plan
- Technology Standards
- Build models & plans
- Environment requirements and specifications for build, test, release, training, disaster recovery, pilot and deployment
- Release policy and release design from Service Design
- Release and deployment models including template plans
- Exit and entry criteria for each stage of release and deployment.
Outputs
- Release and deployment management plan
- Completed RFCs for the release and deployment activities
- Notifications
- Updated service catalogue with the relevant information about the new or changed service
- New or changed service reports
- Deployment ready release package (baselined) for future deployments
Release and deployment Management Process
Generic Release and deployment Management Process
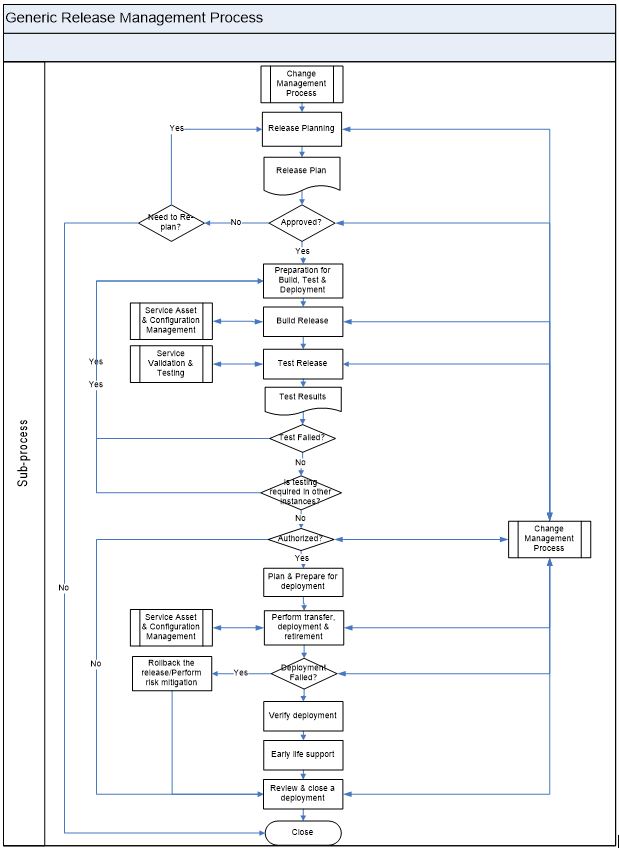
| Activity No. | Step | Description | Input/Output | Role |
| 1 | Release Planning | Detailed Plan should be prepared for release and deployment management. Release planning should be done according to the published release calendar. Release and deployment management plan should be authorized through Change management. Refer: <Release Management Plan – Template> for detailed planning activities. | Input RFC Release calendar Output Release Management Plan |
Release Manager |
| 2 | Approved? | Release plan will be assessed and reviewed by the change management (CAB). If the CAB rejects the release to make the changes in the plan, then plan will be revised and sent for the approval. |
Input Release management plan Output Approval |
CAB |
| 3 | Preparation for Build, Test & Deployment | Before starting the build & test stage release deign should be validated against the requirements. Also the training needs will be identified for the release deployment, build and test teams. | Input Release management plan Output Training needs Validation report |
Release Manager |
| 4 | Build Release | Release and build documentation should be prepared. Input Configuration Items will be acquired tested. Prepare the Release Package. Build & test environments should be managed. Build the release package. | Release Packaging & Build Manager | |
| 5 | Test Release | Testing activities are coordinated through Test Management. Testing aims to build confidence in the service capability. | Input Release Management Plan Release Package Build Output Test Results |
Release Packaging & Build Manager |
| 6 | Test Failed? | If the test is failed then, we need to build the release and proceed with the testing. This will continue till the test is successful. If the tests are successful, then the test results will be sent for the authorization to the change management. | Input Test Results Output Build |
Release Manager |
| 7 | Authorized? | Release plan along with the test results will be sent for the authorization. This activity will be carried out by Change Management. If the release is authorized it will be passed on to the deployment team. If the release got rejected, then the release record will be closed. | Input Release management plan Test Results Output Authorization Rejection |
Change Manager |
| 8 | Plan & Prepare for deployment | Planning & preparation activities will prepare the deployment group for deployment. The Overall approach for this will be prepared as part of the Release management Plan. Deployment assessment will be revisited to check the readiness. | Input Release Management Plan Output Issues, Risks, Impacts, Assessment |
Deployment Staff |
| 9 | Perform transfer, deployment & retirement | The following activities will be performed in the order specified in the deployment plan: Transfer financial assets. Transfer/transition business and organization Deploy process & material Deploy Service management capability Transfer service Deploy the service Decommission and service retirement Removal of redundant assets | Input Release management plan Output Deployed Service |
Deployment Staff |
| 10 | Deployment Failed? | During the phase (5.1.9) if the deployment is failed, then the release should be backed-out/ risk mitigation methods should be followed as per the Release Management Plan. | Input Release Management Plan Output Back-out Deployed Service Risk mitigation |
Deployment Staff |
| 11 | Verify deployment | When the deployment activities are completed, it is important to verify that the users, operations & other staff are capable of using the service. Successful confirmation of the deployment verification will trigger early life support. | Input Deployed Service Output Issues Confirmation |
Deployment Staff |
| 12 | Early life support | Early life support provides an opportunity to transition the new or changed service to Operation in a controlled manner and establish the new service capability and resources. During this stage, support staff resolves operational issues, team implements improvements and resolves problems that help to stabilize the service. | Input Deployed Service Output Operational issues Problem Resolutions Metrics |
Early life support staff |
| 13 | Review & close a deployment | The deployment will be concluded with a handover of the support for the deployment group or target environment to operations. | Input Deployed Service Output Handover |
Release and deployment Management manager |
| 14 | Is testing required in other instances? | After the successful testing of the release, there should be a check to test/deployment in the other instances. | Input Test results Test instances Output Handover |
Release and deployment Management manager |
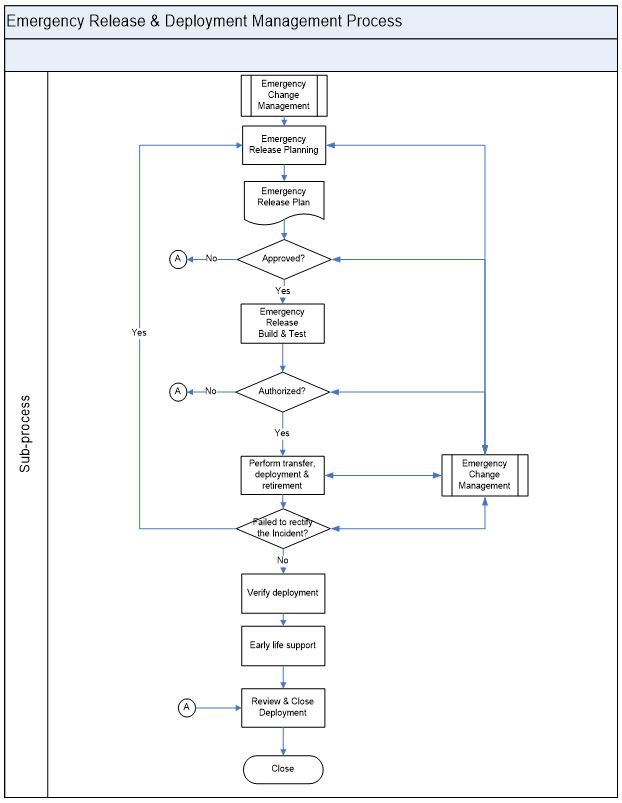
Emergency Release and Deployment Management Process
Emergency release is reserved for releases intended to repair an error in an IT service that is negatively impacting the business at a high degree.
Emergency release management process will follow the normal release management processes and will be governed by Emergency Change management.
References
- Procedure for Change Management
- Procedure for Service Asset & Configuration Management
- Procedure for Service Validation and Testing
Measurements
Reports are generated based on the below metrics.
| Metrics | Description |
| No. of Incidents in Production environment | The number of incidents detected in the live environment that can be attributed to Releases, which need only be measured during the first few months after being released, classified by defect type. |
| No. of Assets introduced | The number of new, changed and retired Assets introduced by the new Release – e.g. how many modules and programs. |
| Planned Vs Actual | Number of releases compared with planned releases. |
| Reduction in Resources & Costs | Reduced resources and costs to diagnose and fix incidents & problems in deployment & production. |
| Reduction in Configuration management defects | Reduced discrepancies in configuration audits. |
| Customer Satisfaction | Increased customer & user satisfaction with the services delivered. |
Authored by Vijay Chander – All rights Reserved – 2023