Manufacturing Use Cases to Implement Now!
Manufacturing Use Cases
As the recent pandemic has taught us, businesses have to be prepared to face a host of unexpected twists and turns and be ready for them. This is very prevalent in the Manufacturing industry, that is the backbone of the world’s economy. As input costs rise, supply chain optimization becomes a key component to keep you competitive. With ageing IT infrastructure, the challenge becomes even more daunting to keep pace with technological advances, train your staff, adapt to new realities. RPA, which has been around for a while is a good start to many of these manufacturing units to take the initial step for cost-cutting while maximizing your ROI. Manufacturers are increasingly moving to wards digital transformation – which is based on Intelligent automation. Intelligent automation allows organizations to focus on standardization and fault free recording of information thereby freeing staff to focus on more strategic activities.
Though there are many situations in the usage of intelligent automation and RPA use cases in manufacturing – I am listing out 4 key areas
- Digitizing operations,
- Automated supply chains,
- Wide usage of Internet of Things (IoT), and finally
- Back-office systems
Digitizing Operations
Let us take a look at 2 key components required in Manufacturing – Production tracking and Bill of Materials (BOM)
Production Tracking in Real time: As the image indicates, today – Using intelligent automation, manufacturers can develop a near real-time overview of progress on orders and the ongoing need for components or raw materials. Manufacturers can adopt lean manufacturing methodologies that optimize scarce resources and keep margins low.

Bill of Materials: Maintaining an accurate bill of materials (BOM) is important and critical for manufacturers. The BOM contains the list of raw materials, sub-assemblies, intermediate assemblies, sub-components, parts, and the quantities of each component required to manufacture an end product. Using intelligent automation, manufacturers can accurately extract product data and replicate human steps required to generate an error-free BOM in a shorter timeframe.
Optimizing Supply Chains
Demand Planning: “Demand planning is a supply chain management process that enables a company to project future demand and successfully customize company output — be it products or services — according to those projections”. Predicting demand of goods and materials across multiple geographies in the supply chain requires effective digital integration and connections. Automation breaks down supply chain silos and provides insight, so goods and materials are ready where they’re required. This becomes even more important when the geographies are spread across countries or continents. A BOT can take on the responsibility of a team member by pulling in information from various sources and provide input to the shift manager so that the optimal production is achieved and the plan is available before the shift starts.
Freight and Transportation Management: Most factory floor operations have tons of data on products in the system. However the interfaces to these are not easy and require a series of steps by dedicated teams to interact with Freight systems which are external. Intelligent automation helps in navigating through these in a effective manner which is a good place to start your RPA implementation.
Inventory Management: Digital workers or BOTS are able to capture the information better than humans. This helps in advance warnings about stock replenishment so that the company does not face stock-outs which affects manufacturing. This is one area where RPA helps by providing timely information about the status of the Inventory in real time so that appropriate measures are taken. Automatic generation of purchase orders are part of this process.
IoT
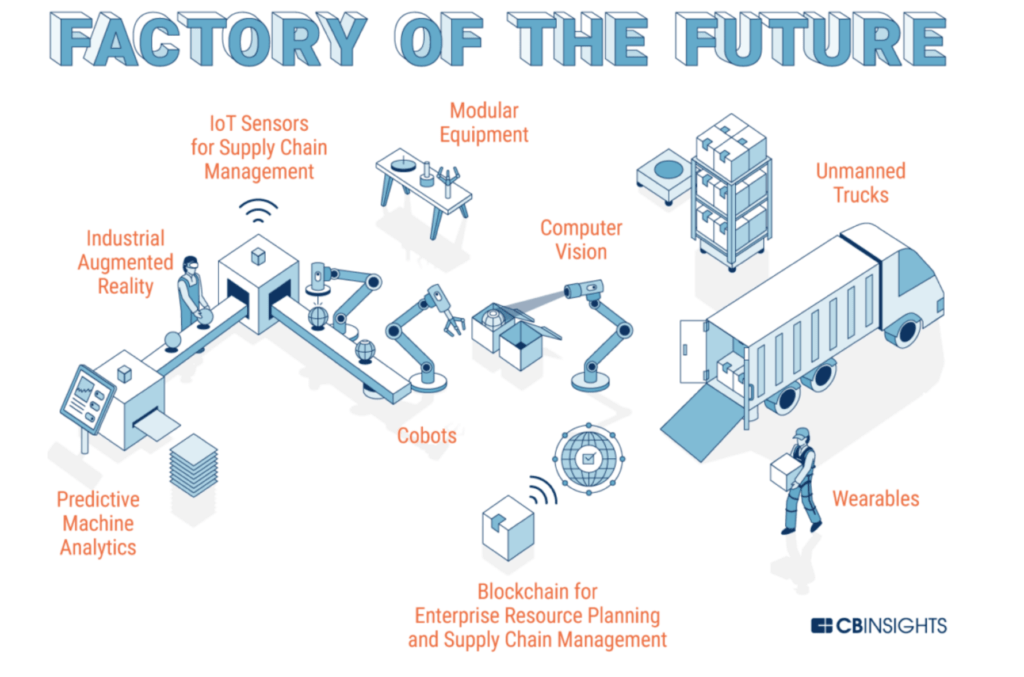
IoT are becoming common place in preventive maintenance activities and act as sensors in supply chain management. Using advance machine learning along with RPA allows faults to be predicted with a high degree of accuracy thereby bringing the downtime of a machine or an assembly and alternatives the uptime of the machinery at a lower maintenance cost. This is but one area and IoTs are invading the manufacturing sector, from everything from temperature control, to counting, to detect defective products and send signals in real time.
Back Office in Manufacturing
While the specialization of manufacturing is the USP of any product organization and they have effective robotic excellence, the back office is sadly staffed with people who are prone to make mistakes. Many of these tasks can now be automated using RPA significantly reducing the errors. Some of the areas to consider in the back office for RPA include the following:
- Invoice Automation
- Order Management
- Contract Management
- Collections
- Vendor and Contractor Onboarding
- Performance Reporting
Here us a diagram to showcase an Invoice automation using RPA
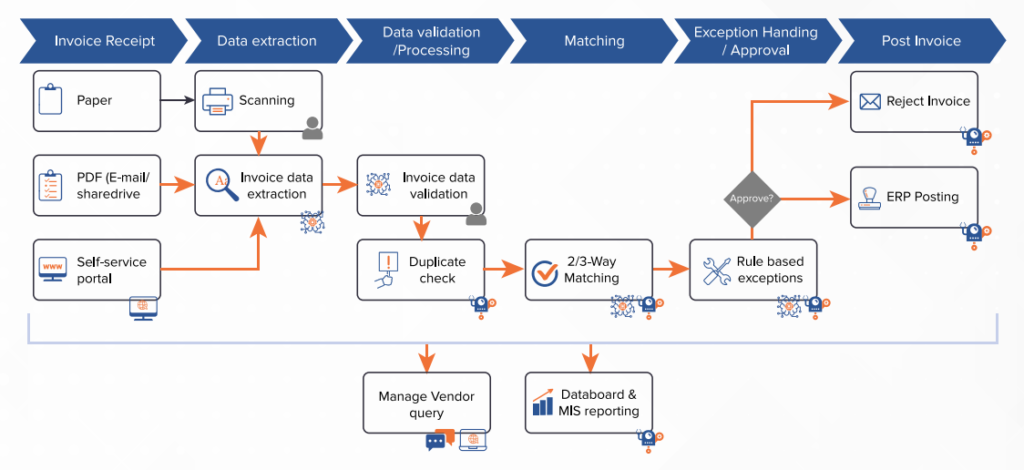
With these many opportunities available, many organizations have already got a head start in implementing these. Why wait? Take the step and start to plan your RPA implementations.
Authored by Vijay Chander – 2023

