
Managing Project Status
Managing Project Status
As the project is being executed, it is extremely important to report on the project in terms of adherence to planned activities, maintaining the schedule, quality, resourcing and financials Managing Project status will ensure that any deviation is reported and addressed as soon as possible to avoid any project delays. There are several components that one needs to manage and let us discuss them here.
Firstly let us know the key persons who are involved in the management of Project Status. Here is the list.
Owners
– Project Manager
– Project Lead
Participants
– Client Project Manager
– Client Stakeholders
– PMO
– Practice Heads
– Sales Manager Account Manager
Let us look into what are the key documents that you look at when you manage project status.
- Project Plan
- Financials
- Quality & Client Perception
- Scope
- Resource Plan
- Status Reports
Project Plan
A well-constructed project plan serves as the cornerstone of successful project management, playing a pivotal role in guiding teams toward achieving their goals. It acts as a roadmap, providing a structured framework that outlines tasks, timelines, and resource allocations. The importance of a project plan lies in its ability to establish clear objectives, define roles and responsibilities, and anticipate potential challenges. This proactive approach enables teams to mitigate risks, allocate resources efficiently, and maintain a cohesive focus on the project’s overarching objectives. Additionally, a comprehensive project plan enhances communication among team members, stakeholders, and leadership, fostering a shared understanding of project milestones and expectations. Overall, the project plan not only acts as a strategic tool for effective coordination but also empowers teams to adapt to changes, adhere to timelines, and deliver successful outcomes.
It becomes imperative that the project manager keeps focus on the project plan. Updating and monitoring it closely as this is the basis for generating several other key reports.
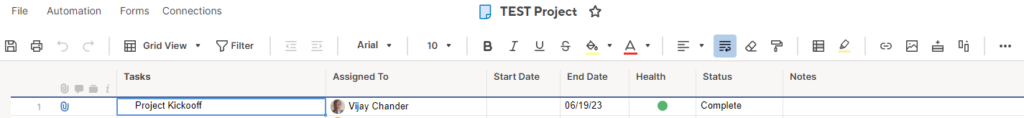
There are many tools you can use, the popular ones being Microsoft Project and Smartsheet.
Financials
In an IT project, tracking various financial aspects is crucial to ensuring effective budget management and project success. Key financials to monitor include initial project costs, encompassing expenses related to hardware, software, and infrastructure acquisition.
Ongoing operational costs, such as licensing fees, maintenance, and support contracts, should also be meticulously tracked. Labor costs, covering salaries, benefits, and any additional personnel-related expenses, play a significant role in overall budget considerations. It is essential to monitor and control project spending against the allocated budget, allowing for real-time adjustments as needed. Additionally, unforeseen expenses, potential cost overruns, and return on investment (ROI) metrics should be closely scrutinized to make informed financial decisions.
By diligently tracking these financial elements, project managers can maintain fiscal transparency, optimize resource utilization, and ensure that the IT project aligns with organizational goals while staying within the predefined financial constraints.
Quality and Client Perception
Quality in a project is not merely the absence of defects but the presence of excellence in every aspect of the deliverables. At your organization, you prioritize a meticulous approach to quality management in every project you undertake. You should understand that client perception is closely intertwined with the quality of your work.
By adhering to industry best practices, conducting rigorous testing, and implementing robust quality assurance processes, you would aim not only to meet but exceed client expectations. Consistent communication, feedback loops, and a client-centric mindset ensure that your projects not only meet technical requirements but also align with the broader strategic objectives of your clients.
Your organization should recognize that client perception is a reflection of the value you bring, and your commitment to delivering high-quality solutions fosters trust, satisfaction, and long-term partnerships with your clients.
Scope
Effectively managing the scope of a project is paramount to its success, serving as a linchpin for project control and client satisfaction. Scope management involves defining, documenting, and controlling the project’s boundaries, deliverables, and requirements. By clearly outlining what is within and outside the project’s scope, teams can prevent scope creep, which can lead to delays, budget overruns, and diminished quality.
A well-defined scope not only establishes a solid foundation for project planning and execution but also aids in resource allocation and risk mitigation. Additionally, managing scope facilitates better communication and expectations among project stakeholders, aligning everyone on the project’s objectives. Successfully navigating scope management ensures that project teams deliver what was promised, on time, and within budget, fostering client satisfaction and enhancing the overall project outcome
Resource Plan
A resource plan is a critical component of effective project management, providing a comprehensive roadmap for allocating and utilizing resources throughout the project lifecycle.
By systematically detailing the human, financial, and material resources required, a resource plan enables teams to optimize efficiency and avoid bottlenecks. It ensures that the right personnel are assigned to specific tasks, preventing overloading or underutilization of team members. Financial resources are judiciously allocated, aligning with budget constraints and project priorities.
Furthermore, a well-constructed resource plan helps in identifying potential resource gaps or constraints in advance, allowing for proactive solutions and risk mitigation. Overall, the resource plan is instrumental in enhancing project transparency, promoting effective communication, and ultimately contributing to the successful delivery of projects within scope, time, and budget constraints.
Status Report
Status reports are a vital communication tool in project management, offering a concise snapshot of project progress, challenges, and upcoming milestones. These reports provide stakeholders, including team members and leadership, with real-time insights into the project’s health, enabling informed decision-making. By fostering transparency, status reports enhance accountability, alignment, and the overall likelihood of successful project outcomes.
KPIs
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in a status report provide a quantitative and qualitative measure of a project’s progress. I personally like to provide status reports based on KPIs. Some essential KPIs to track in a status report include:
- Timeline Adherence: Monitor project milestones against the planned schedule to assess if the project is on track and meeting deadlines.
- Budget Variance: Track financial metrics to ensure that the project is within budget. This includes monitoring actual spending against the allocated budget.
- Resource Utilization: Evaluate the efficiency of resource allocation by tracking team members’ workload, identifying potential bottlenecks, and ensuring optimal use of available resources.
- Task Completion Rate: Measure the completion of individual tasks or project phases to gauge overall progress and identify areas that may need additional attention.
- Risk and Issue Management: Highlight and assess the status of identified risks and issues, including their resolution status and any emerging concerns that may impact the project.
- Quality Metrics: Assess the quality of deliverables by tracking relevant metrics, such as defect rates, customer satisfaction, or adherence to predefined quality standards.
- Stakeholder Communication: Evaluate the effectiveness of communication by monitoring stakeholder engagement, feedback, and overall satisfaction with project updates.
- Scope Changes: Document and analyze any changes to the project scope, ensuring that alterations are carefully evaluated for their impact on timelines, budgets, and overall project goals.
- Team Productivity: Measure team productivity through metrics like completed tasks per unit of time, identifying trends that can inform resource adjustments or additional support.
- Customer Satisfaction: Incorporate feedback from end-users or clients to gauge satisfaction levels, ensuring that the project aligns with their expectations and requirements.
The six items above help to manage project status.
Authored by Vijay Chander – All rights reserved 2023.

