A Guide to Knowledge Management Process
What is Knowledge Management?
Purpose & Scope
Purpose
The purpose of Knowledge Management process is to ensure that the right information is delivered to the appropriate place or competent person at the right time to enable the informed decision.
Scope
Scope includes the management of the information & data using which sufficient knowledge will be derived to support the agreed <Customer name>’s Services.
Note:
Detailed attention to the capturing, maintenance and use of asset & configuration data is under the scope of Change Management Process.
Definitions
Data
It is a set of discrete facts about event.
Information
Information comes from providing context to data.
Knowledge
Knowledge is composed of the tactic experiences, ideas, insights, values & judgements of individuals.
Wisdom
Wisdom gives the ultimate discernment of the material and having application and contextual awareness to provide a strong common sense judgement.
Knowledge Management
It is the process responsible for gathering, analyzing, storing and sharing knowledge and information within your Service Delivery systems
Service Knowledge Management System (SKMS)
It is a set of tools and databases that are used to manage knowledge and information. The SKMS includes the Configuration Management System (CMS), Known Error Data Base (KEDB) as well as other tools and databases. The SKMS stores, manages, updates, and presents all information that an IT Service provider needs to manage the full Lifecycle of <Customer Name>’s IT Services.
Roles and Responsibilities
Knowledge Management Process Owner
Responsibilities
- Undertakes the Knowledge Management (KM) role, ensuring compliance with the organization’s policies and processes.
- Is the architect of knowledge identification, capture and maintenance
- Identifies, controls and stores any information deemed to be relevant to the services provided, which is not available via any other means.
- Maintains the controlled knowledge items.
- Ensures all knowledge items are made accessible to those who need them in an efficient and effective manner.
- Monitors publicity regarding the knowledge information to ensure that information is not duplicated and is recognized as a central source of information etc.
- Acts as an adviser to business and IT personnel on KM matters, including policy decisions on storage, value, worth etc.
Input, Output
Inputs
- Errors detected during transition
- Problem Management data
- IT Service Management data
Outputs
- Service Knowledge Management System
Knowledge Management Process
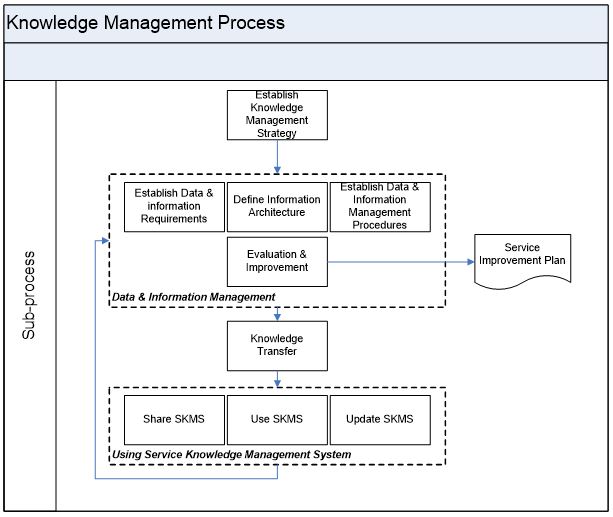
| Activity No. | Step | Description | Input-Output | Role |
| 1 | Establish KM Strategy | An overall strategy for KM is required. Refer: <Knowledge Management Strategy – Template> | Output KM Strategy | KM Process Owner |
| 2 | Establish Data & information Requirements | Efficiency and effectiveness are delivered by establishing the requirements for information. Establish the designated data and information items, their content and form, together with the reason, e.g. technical, project, organizational, Service Management process, agreement, operations and information. Establish the requirements for data protection, privacy, security, ownership, agreement restrictions, rights of access, intellectual property and patents with the relevant stakeholder. Define who needs access to what data and information as well as when they access it. Consider any changes to the Knowledge Management process through Change Management. | Input KM Strategy Output Data & Information Requirements |
KM Process Owner |
| 3 | Define Information Architecture | In order to make effective use of data, in terms of delivering the required knowledge, a relevant architecture matched to the situation and the knowledge requirements is essential. Create and regularly update a Service Management information model that enables the creation, use and sharing of information that is flexible, timely and cost effective. Define systems that optimize the use of the information while maintaining data and information integrity. | Input Data & Information Requirements KM Strategy data classification schemes Output Information Architecture |
KM Process Owner |
| 4 | Establish Data & Information Management Procedures | When the requirements and architecture have been set up, data and information management to support Knowledge Management can be established. Establish mechanisms to: | Input Output | Knowledge Management Process Owner |
| 5 | Evaluation & Improvement | As with all processes, the capture and usage of data and information to support Knowledge Management and decision making requires attention to ongoing improvement. | Input Service Knowledge Management System Output Improvement opportunities | Knowledge Management Process Owner |
| 6 | Knowledge Transfer | During the service lifecycle, need to focus on retrieving, sharing and utilizing their knowledge through problem solving, dynamic learning, strategic planning and decision making. To achieve this, knowledge needs to be transferred to other parts of the organization at specific points in the lifecycle. | Input Requirements for Knowledge Output Knowledge Transfer | Knowledge Management Process Owner |
| 7 | Using Service Knowledge Management System | Service Knowledge Management System will be shared, updated & used to provide services to customers. | Input SKMS Output Knowledge transferUpdates to SKMS | Service Management Teams/ Knowledge Management Process Owner |
References
- Procedure for Service Asset & Configuration Management
- Procedure for Incident Management
- Procedure for Problem Management
- Procedure for Change Management
Measurements
Knowledge Management is an enabling process and so demonstration of its effectiveness needs to be inferred from indirect measurement.
Reports are generated based on the below metrics.
| Metrics | Description |
| No. of Knowledge-related Errors | Successful implementation and early life operation of new and changed services with few knowledge-related Errors. |
| Reduced time & effort to support | Reduced time and effort required to support and maintain services. |
| Speed of access to information | Reduced time to find information for diagnosis and fixing incidents and problems. |
| Reduction in Person dependency | Reduced dependency on personnel for knowledge. |
| Reduction in Incident Resolution Time due to knowledge base | Lower incident, problem and error resolution times influenced by better targeted support staff training and by a relevant, maintained and accessible knowledge base containing workarounds. |
| Reduction in Early life support & transition time | Reduced time for transition and duration of early life support. |
| No. of Incidents caused due to lack of knowledge | Incidents and lost time categorized as ‘lack of user knowledge’ |
| No. of incident resolved by referring to Knowledge Base | Incidents related to new or changed services fixed by reference to knowledge base. |
| Usage of SKMS | Usage of the knowledge base, measured by: Number of accesses to the SKMSAverage time taken to find materials |
| Errors reported regarding SKMS | Errors reported by staff or detected at audit (none probably means no one was using it) |
| Updating the Knowledge Base | Involvement of staff in discussion/query/answer forums providing support through knowledge sharing and capture of that shared knowledge |
| Re-usable material | Degree of re-use of material in documentation such as procedures, test design and service desk scripts |
| Feedback on Knowledge Transfer | Satisfaction with training courses, newsletters, web briefings etc. |
Authored by Vijay Chander – All rights Reserved – 2023

