The Change Management Process explained!
The Change Management Process explained
Purpose & Scope
Purpose
The purpose of Change Management process is to ensure that:
- Standardized methods and procedures are used for efficient and prompt handling of all changes to the <Customer’s Name>’s IT service.
- All Changes to <Customer’s Name>’s service assets & configuration items are recorded in the Configuration Management System.
- Overall <Customer’s Name>’s business risk is optimized.
Scope
Scope of the Change Management Process includes the following:
Definitions
Configuration Item
Configuration Item is any component that needs to be managed in order to deliver <Customer’s Name> IT Service.
Request for Change (RFC)
This is the formal change request, including a description of the change, components affected, business need, cost estimates, risk assessment, resource requirements, and approval status.
Service Asset
It can be any Resource or Capability that contribute to the delivery of a service.
Assets can be of the following types: Management, Organization, Process, Knowledge, People, Information, Applications, Infrastructure and financial capital.
Change Initiator
A person who initiates a request for change; this person can be a business representative or a member of the IT organization.
Change Advisory Board (CAB)
The CAB is a cross-functional group set up to evaluate change requests for business need, priority, cost/benefit, and potential impacts to other systems or processes. Typically the CAB will make recommendations for deployment, further analysis, deferment or cancellation.
Emergency Change Advisory Board (ECAB)
It is the subset of the CAB that deals only with Emergency Changes. It is established to be able to meet on short notice to authorize or reject changes with emergency priority.
Roles and Responsibilities
Change Manager
Responsibilities
- Receives, Logs and allocates a priority, in collaboration with the Change Initiator, to all RFCs; rejects any RFCs that are impractical.
- Tables all RFCs for a CAB meeting; issues an agenda and circulates all RFCs to CAB members in advance of meetings to allow prior consideration.
- Decides which people will come to which meeting, who gets specific RFCs depending on the nature of the RFC, what is to be changed and people’s areas of expertise.
- Organize ECAB meetings for all Emergency RFCs.
- Chairs all CAB & ECAB meetings.
- After consideration of the advice given by the CAB or ECAB, authorizes acceptable changes.
- Issues change schedules, via service desk.
- Liaises with all necessary parties to co-ordinate change planning, building, testing & implementation.
- Updates the change log with all progress that occurs.
- Reviews all the implemented changes to ensure that their objectives.
- Analyses change records to determine any trends or apparent problems that occur; seek rectification with relevant parties.
- Review all pending RFCs.
- Close RFCs.
- Produces regular & accurate management reports.
Change Authority
Formal change authorization is obtained for each change from change authority that may be a role, person or a group of people. The levels of authorization for a particular type of change should be judged by the type, size & the risk of the change.
Responsibilities
- Authorizes the Change based on the type, size, risk, anticipated business risk, financial implications and the scope of the change.
Change Advisory Board
Responsibilities
- Assists change management in the assessment and prioritization of the changes.
- Consider and recommend the adoption or rejection of changes appropriate for higher level authorization and then recommendations will be submitted to the change authority.
- Recommend the follow-up actions for the emergency changes and the changes implemented as workarounds to incidents.
Input, Output
Inputs
- Request For Change (RFC)
- Configuration Management System (CMS)
- Change Schedule (CS)
- Test results, test reports & evaluation reports
- Change & Release policies
- Change, Transition, Release, Deployment, Test, Evaluation & Remediation plans
Outputs
- Approved/Rejected RFCs
- New, changed or disposed assets or configuration items
- Request For Change (RFC)
- Change Schedule (CS)
- CAB/ECAB meeting minutes & actions
- Management Information (Reports)
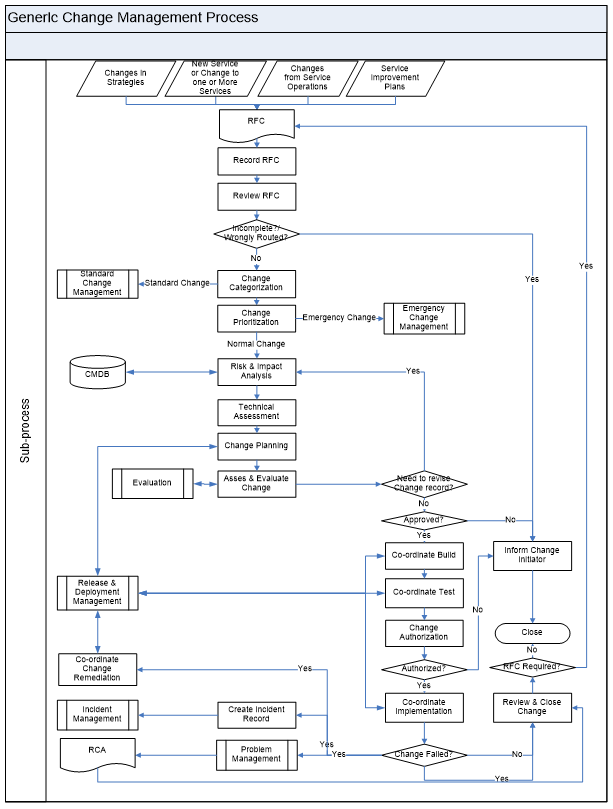
Change Management Process
Generic Change Management Process
| Activity No. | Step | Description | Input/Output | Role |
| 1 | RFC | A change is raised by a request from the initiator – the individual or the organizational group that requires the change. It can be triggered from various service lifecycle phases. | Input RFC | Change Initiator |
| 2 | Record RFC | RFC should be recorded and allocated a unique identification number. | Input RFC Output Change Record | Change Manager |
| 3 | Review RFC | Change management should briefly consider each request and filter out any that seems to be: Totally Impractical, Repeats of earlier RFCs, accepted, rejected or still under consideration. | Input Change Record Output Accepted/Rejected | Change Manager |
| 4 | Incomplete? /Wrongly Routed? | If the RFC found to be Incomplete? /Wrongly Routed? Then inform the initiator and close the change record. | Input Output | Change Manager |
| 5 | Change Categorization | All changes should be categorized. If the change identified as the standard change then standard change management process should be followed. Refer: <Standard Change Matrix – Template> | Input Change Record Output Categorization Standard Change | Change Manager |
| 6 | Change Prioritization | All the changes should be prioritized based on the impact & the urgency of the change. If the change is an emergency change then follow the emergency change management process. Refer: <Change Priority Matrix – Template> | Input Change Record Output Prioritization Emergency Change | Change Manager |
| 7 | Risk & Impact Analysis | All the changes should be assed for Risk & impact of the change. Impact can be identified by referring CMS. Refer: <Change Impact & Risk categorization Matrix> | Input Change record Output Risk Impact | Technical team/ Change Manager |
| 8 | Technical Assessment | Technical assessment should be done to check the technical feasibility to implement the change. | Input Change record Output Technical Assessment | Technical team/ Change Manager |
| 9 | Change Planning | Change should be planned for build, test, implementation & remediation. This activity should be carried out with the help of “Release & Deployment Management”. | Input Change record Output Change Plan | Technical team/ Change Manager |
| 10 | Asses & Evaluate Change | All the changes should be assessed and evaluated and approved. CAB will asses & evaluate all the planned changes. If the results are not satisfactory then CAB will instigate the Change planning activities. | Input Change record Output Approved Rejected | CAB |
| 11 | Co-ordinate Build | After the approval from CAB, change should be built in order to test the change. This activity should be carried out with the help of “Release & Deployment Management”. | Input Change record Output Build | Change Manager |
| 12 | Co-ordinate Test | After the change is built, change should be tested & the results will be published. This activity should be carried out with the help of “Release & Deployment Management”. | Input Change record Output Test results | Change Manager |
| 13 | Change Authorization | Test results & the change plan will be sent for the authorization. Level of the authorization will be decided based on the type, risk & impact of the change. Refer: <Change Authorization Matrix – Template> | Input Test Results Change record Output Authorization | Change Manager |
| 14 | Co-ordinate Implementation | Once the change is authorized, change will be implemented as per the planned schedule. This activity should be carried out with the help of “Release & Deployment Management”. | Input Change record Authorization Output Change Implementation | Change Manager |
| 15 | Change Failed? | If the change is failed, then Change remediation plan should be instigated. An incident record will be raised for the further investigation. A Problem record will be raised for RCA and will be reviewed during the Change Review. Existing change record will be reviewed & closed. | Input Change record Implementation results Output Change Closure Incident | Change Manager |
| 16 | Co-ordinate Change Remediation | If the change is failed, then the remediation plan should be implemented to bring the service into the earlier status. This activity should be carried out with the help of “Release & Deployment Management”. | Input Change record Change remediation plan Output Remediation | Change Manager |
| 17 | Review & Close Change | All the implemented changes should be reviewed and the necessary actions should be triggered. Changes will be reviewed in the CAB meetings. | Input Output | Change Manager |
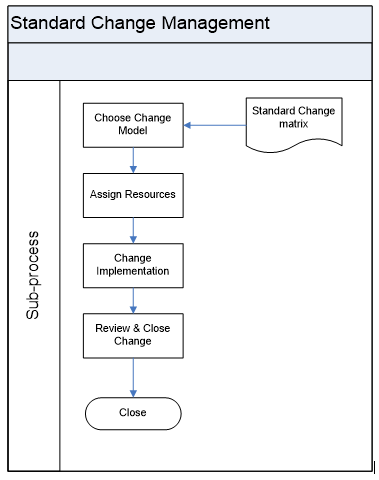
Standard Change Management Process
| Activity No. | Step | Description | Input/Output | Role |
| 1 | Choose Change Model | Standard changes are changes to the services for which the approach is pre-authorized by change management that has an accepted and established procedure to provide specific change requirement. Change models will be created to implement the standard changes. Refer: <Standard Change Matrix – Template> | Input Standard Change Output Change Model | Change Manager/Service Desk/Technical Team |
| 2 | Assign Resources | Resources will be assigned as per the requirement to implement the change | Input Standard Change Output Resource Allocation | Change Manager |
| 3 | Change Implementation | Change will be implemented using the change model and the results will be communicated to the Change Initiator. | Input Standard ChangeChange Model Output Change Results | Service desk/Technical Team |
| 4 | Review & Close Change | All the implemented changes should be reviewed and the necessary actions should be triggered. | Input Change record Output Improvement Actions | Change Manager |
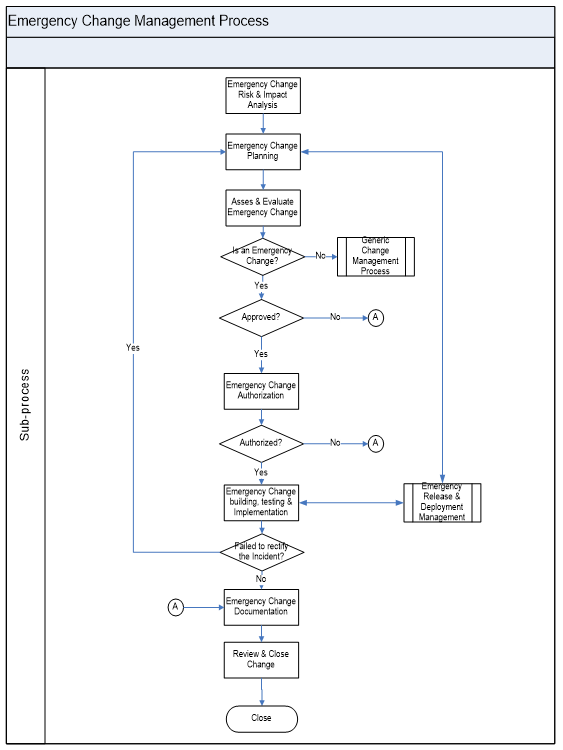
Emergency Change Management Process
Emergency change is reserved for changes intended to repair an error in an IT service that is negatively impacting the business at a high degree.
Emergency Change management process will follow the normal change management processes expect that:
- Approval will be given by the ECAB rather that waiting for a CAB meeting.
- Testing may be reduced, or in extreme cases forgone completely, if considered a necessary risk to deliver the change immediately.
- Documentation of the change record and configuration data may be deferred, typically until normal working hours.
References
- Procedure for Release & Deployment Management
- Procedure for Service Asset & Configuration Management
- Procedure for Incident Management
- Procedure for Problem Management
- Procedure for 7-Step Improvement Process
Measurements
Reports are generated based on the below metrics.
| Metrics | Description |
| Benefits of the change | Benefit of Change = (Value of Improvements) + (Negative impacts prevented or terminated) – (Cost of the Change Process) |
| Unauthorized changes | Reduction in the number of unauthorized changes |
| Backlog Changes | Reduction in backlog of change requests |
| Unplanned changes/Emergency fixes | Reduction in the number and percentage of unplanned changes and emergency fixes |
| Change Success Rate | Percentage of changes implemented successfully |
| Remediation of changes | Reduction in the number of changes where remediation invoked |
| Failed Changes | Reduction in number of failed changes |
| Change Implementation Time | Average time to implement based on urgency/priority/type. |
| Incidents caused by changes | Incidents attributable to the changes |
| Change Estimation | Percentage accuracy in change estimation |
| Impact assessment | Number of changes implemented with incomplete impact assessment |
| Frequency of the changes | Frequency of the changes by service, business unit etc. |
| Change Volume | Volume of the changes & trends |
| Planned Vs Unplanned | Ration of planned Vs unplanned changes |
| Accepted Vs Rejected | Ratio of Accepted to rejected change requests |
Authored by Vijay Chander – All rights reserved 2023