
Automation Maturity Curve
Automation Maturity Curve
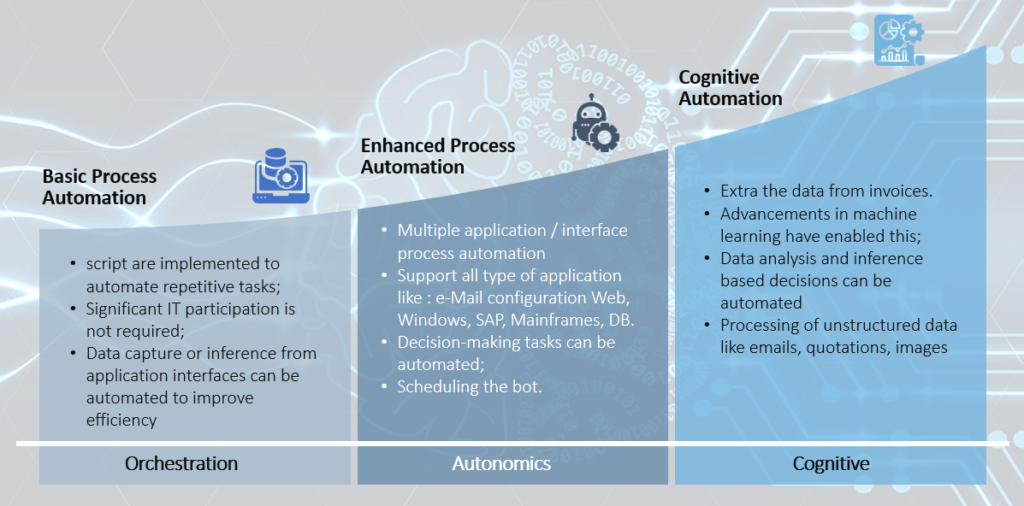
Automation Maturity Curve – Where is your organization on this infographic? Many companies are already involved in the Basic Process automation . Take the leap to the next step for Enhanced Process automation by integrating your major ERP applications by building some intelligence into it. Finally leap into Cognitive automation dealing with your unstructured data and building AI using ML. Look for more of these articles in this site. Let us have some understanding of the three types described in the automation maturity curve.
Basic Process Automation
Basic process automation involves automating repetitive, rule-based tasks such as data entry, file transfers, or simple workflows. It focuses on increasing efficiency by eliminating manual tasks, allowing employees to focus on higher-value work. These automations typically operate in isolation, handling individual tasks or processes with minimal interaction between systems.
In contrast, orchestration takes automation to the next level by coordinating multiple automated tasks across different systems, applications, or departments. It ensures that these automated processes work together seamlessly, managing dependencies and ensuring that data flows smoothly between tasks. This integrated approach enables businesses to automate more complex workflows, improving overall operational efficiency and scalability.
Enhanced Process Automation
Enhanced process automation involves automating more complex, decision-based tasks, often leveraging AI, machine learning, and advanced algorithms. Unlike basic automation, which focuses on rule-based tasks, enhanced automation can adapt to changing conditions and make intelligent decisions without human intervention. This level of automation is often referred to as “autonomics,” where systems can self-regulate, self-heal, and optimize processes in real time.
Autonomics enhances automation by adding layers of intelligence and adaptability, allowing systems to predict issues, resolve problems, and adjust workflows autonomously. This reduces the need for manual oversight and allows organizations to handle dynamic, unpredictable scenarios with greater efficiency and accuracy. By integrating autonomic capabilities, businesses can achieve a higher level of operational agility and resilience.
Cognitive Automation
Cognitive automation refers to the advanced automation of complex processes that require human-like reasoning, understanding, and decision-making capabilities. By leveraging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and natural language processing, cognitive automation can analyze vast amounts of unstructured data and provide insights that drive intelligent actions. This evolution from basic automation allows organizations to automate not just repetitive tasks, but also intricate processes that involve learning, adaptation, and nuanced decision-making.
Cognitive automation enhances traditional automation by enabling systems to mimic human cognitive functions, allowing them to learn from experiences and improve over time. This means that businesses can automate processes that require judgment and context, such as customer service interactions, fraud detection, and data analysis. As a result, cognitive automation fosters greater efficiency, accuracy, and innovation, empowering organizations to respond swiftly to changing market conditions and customer needs while freeing human employees to focus on more strategic, value-added activities.
Authored by Vijay Chander – All rights Reserved – 2022

